Introduction
Picture this: Your marketing team needs customer data for an upcoming campaign. You submit a request to IT, initiating a complex process that involves multiple teams, approval chains, and coordination across departments. The request joins a backlog of similar requests, each requiring data team resources.
This scenario plays out daily in enterprises worldwide. What should be simple data requests turn into lengthy processes that can stretch for weeks or months.
The bottleneck isn’t technical—it’s organizational. With exploding data volumes across enterprises, traditional request-based models simply can’t keep pace with business needs. The solution?
Self-service analytics is powered by modern data catalogs that put data directly into the hands of those who need it while maintaining proper governance.
In this post, we’ll explore how data catalogs are transforming enterprise data access from lengthy, multi-stage approval processes to efficient self-service experiences.
The Enterprise Data Access Crisis
The traditional data request workflow in large organizations is a complex, multi-stage process that often looks something like this:
- The business user identifies the data needed and submits a request
- Request is reviewed by the data governance team
- The data team evaluates feasibility and required resources
- Security reviews and approves appropriate access levels
- A data engineer locates the data across various systems
- Data is extracted, transformed, and delivered
- Business user finally receives the data
At each handoff point, the request can sit in a queue for days or weeks. The sheer volume of similar requests creates backlogs that stretch timelines even further. In many organizations, this process takes 4-12 weeks from request to delivery—an eternity in today’s fast-paced business environment.
This isn’t just inconvenient; it has real business costs:
- Missed opportunities: By the time data arrives, market conditions have changed
- Reduced agility: Teams can’t quickly test hypotheses or iterate on ideas
- Wasted resources: Data teams spend time on repetitive, low-value tasks
- Decision-making without data: Unable to wait, business users make decisions based on gut feeling rather than facts. I guess we need both :)
As one VP of Data at a Fortune 500 retail company told me, “We had brilliant data scientists spending 60% of their time just finding, understanding, and preparing data for others. It was the most expensive data delivery service imaginable.”
The problem has only intensified with the explosion of data volumes and sources. Most enterprises now manage petabytes of data across cloud data warehouses, data lakes, SaaS applications, and legacy systems. Finding the right dataset is like searching for a needle in a digital haystack—if you don’t know exactly where to look.
What organizations need is a way to empower business users to find and access data themselves, while still maintaining governance and security. This is where data catalogs, particularly modern solutions like Unity Catalog, are transforming the enterprise data landscape.
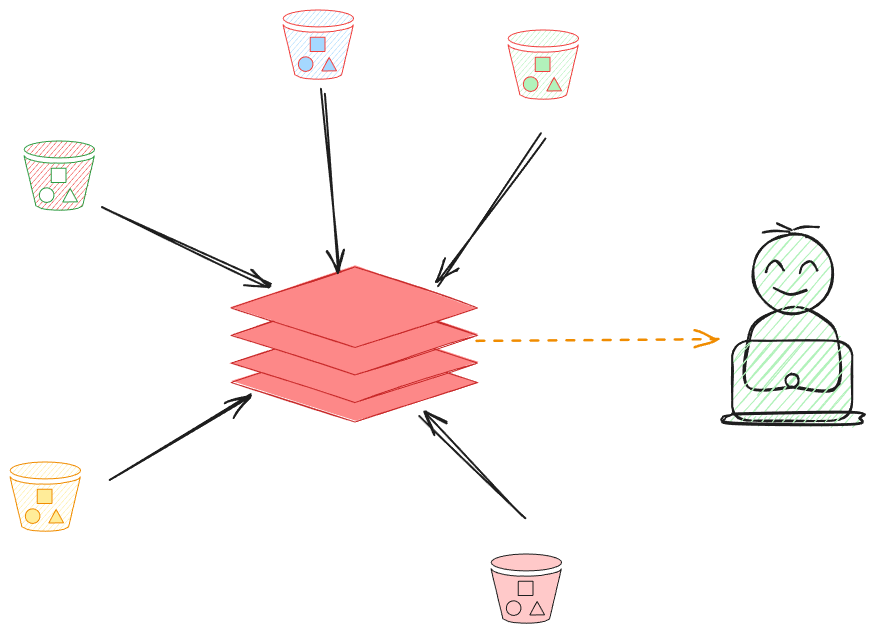
Unity Catalog: A Solution to the Enterprise Data Bottleneck
Data catalogs emerged as a solution to the enterprise data access crisis by providing a central inventory of all data assets. Think of a data catalog as a “Google for your enterprise data”—a searchable index that helps users discover, understand, and access the data they need.
Unity Catalog takes this concept further by providing a unified governance layer that works seamlessly across your entire data estate. Unlike traditional catalogs that often focus solely on metadata management, Unity Catalog combines discovery, governance, lineage, and security in a single solution that integrates with your existing data tools.
The key differentiators that make Unity Catalog particularly effective for enterprise self-service include:
- Unified access control: Apply consistent security policies across all data assets, regardless of where they’re stored
- Easy integration: Works natively with popular analytics and BI tools that business users already know
- Comprehensive coverage: Catalogs structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data from multiple sources
- Fine-grained permissions: Grant access at the database, table, view, or even column level
- Automated metadata extraction: Reduce manual documentation through intelligent metadata harvesting
For enterprises struggling with data access bottlenecks, Unity Catalog offers a path to transform weeks-long data requests into minutes-long self-service experiences—without sacrificing security or governance.
Core Features That Enable Self-Service
Modern data catalogs like Unity Catalog come equipped with several key features that make self-service analytics possible while maintaining proper governance and security. Let’s explore these capabilities and how they empower business users and data teams alike.
Unified Security Model and Fine-Grained Access Control
One of the biggest barriers to self-service has always been security concerns. Traditional approaches often led to either overly restrictive policies that blocked legitimate access or overly permissive ones that created compliance risks.
Unity Catalog solves this through:
- Column-level security: Grant access to specific columns rather than entire tables, ensuring users see only the data they need
- Row-level security: Apply dynamic filters based on user attributes to show only relevant records
- Attribute-based access control: Define policies using business roles and contexts rather than technical identifiers
- Centralized policy management: Maintain security rules in one place that apply consistently across all data assets
This granular approach means organizations can confidently open up data access without compromising sensitive information.
Simplified Data Discovery
Finding the right data is often half the battle. Unity Catalog makes data discovery intuitive through:
- Natural language search: Find data assets using business terminology rather than technical names
- Rich filtering: Narrow results by data domain, owner, certification status, popularity, and more
- Suggested datasets: Smart recommendations based on your role and past usage patterns
- Data previews: Quickly assess if a dataset contains what you need without requesting access
This dramatically reduces the time spent hunting for the right data and eliminates the need to involve data engineers in the discovery process.
Business Glossary and Semantic Layer
Bridging the gap between technical data assets and business meaning is crucial for true self-service. Unity Catalog accomplishes this through:
- Business glossary integration: Link technical columns to business definitions
- Common terminology: Ensure consistent interpretation of metrics and dimensions
- Semantic relationships: Understand connections between different data elements
- Certification badges: Identify trusted, verified datasets endorsed by data stewards
These features help business users understand not just where data is, but what it means and how to use it appropriately.
Data Lineage and Impact Analysis
Understanding where data comes from and how it’s been transformed is essential for building trust. Unity Catalog provides:
- End-to-end lineage visualization: Trace data from source systems through transformations to final consumption
- Column-level lineage: See precisely how specific data elements are derived
- Impact analysis: Before making changes, understand what downstream assets might be affected
- Version history: Track how datasets evolve over time
This transparency builds confidence in data quality and helps users understand the context of the information they’re working with.
Integration with Analytics Tools
Self-service data access is only valuable if users can actually do something with the data. Unity Catalog integrates with:
- Business intelligence tools: Direct connections to Tableau, Power BI, Looker, and more
- Notebooks and data science platforms: Seamless workflows for Python, R, and SQL analytics
- Spreadsheet applications: Direct access for Excel users
- Data preparation tools: Connections to data wrangling and ETL platforms
These integrations mean users can stay in their familiar tools while benefiting from improved data discovery and governance.
By combining these capabilities, Unity Catalog creates an environment where business users can confidently find, understand, and use data on their own terms—while data teams maintain appropriate governance and security controls.
In the next section, we’ll explore practical implementation approaches and real-world examples of organizations that have successfully transformed their data access models with Unity Catalog.
Practical Application: From Months to Minutes with Unity Catalog
Implementing a data catalog is not just a technical deployment—it’s a transformation in how your organization approaches data access. Here’s a practical roadmap for using Unity Catalog to revolutionize data accessibility in your enterprise.
Step 1: Establish a Strong Foundation
Before diving into implementation, lay the groundwork for success:
- Identify key stakeholders: Include representatives from data teams, business units, security, and compliance
- Define success metrics: Establish baseline measurements for data request turnaround times, data team workload, and business user satisfaction
- Map your data landscape: Inventory your key data sources, systems, and existing access patterns
- Clarify governance principles: Determine who can access what data under which circumstances
A multinational financial services company I worked with began by measuring their average data request fulfillment time (17 days) and the percentage of data scientist time spent on data discovery and preparation (42%). These metrics provided clear benchmarks to measure their progress.
Step 2: Start Small but Strategically
Rather than attempting to catalog your entire data estate at once, begin with high-value, frequently requested datasets:
- Select pilot domains: Choose 2-3 data domains with high business impact and reasonable complexity
- Identify internal champions: Find enthusiastic business users who can provide feedback and advocate for adoption
- Implement metadata extraction: Configure automated scanners to pull technical metadata from source systems
- Enrich with business context: Add descriptions, tags, and business definitions to make data meaningful
A retail organization successfully launched their catalog by focusing on their customer and product domains first—addressing the most common data requests before expanding to other areas.
Step 3: Set Up Governance that Enables Rather than Restricts
Effective governance accelerates self-service rather than impeding it:
- Implement tiered access levels: Create clear categories (public, restricted, confidential) with corresponding access procedures
- Automate approval workflows: Where possible, enable automated access grants based on role and purpose
- Design for transparency: Make access policies visible and understandable to end users
- Establish data quality indicators: Help users understand the reliability of different datasets
Unity Catalog’s fine-grained permissions model makes this possible by allowing you to set policies at the column level, ensuring users see only appropriate data.
Step 4: Drive Adoption and Measure Impact
A catalog is only valuable if people use it:
- Provide targeted training: Develop role-specific tutorials that focus on users’ actual workflows
- Integrate with existing tools: Ensure the catalog appears within the tools users already work with
- Create feedback loops: Make it easy for users to report issues and suggest improvements
- Celebrate success stories: Highlight examples where self-service access led to business wins
Real-World Results
Organizations that have successfully implemented data catalogs like Unity Catalog have seen dramatic improvements:
- Airbnb reduced their average data request fulfillment time from 3 weeks to 2 days by implementing a comprehensive data catalog that enabled analysts to self-serve their data needs
- Pfizer increased their “first-time-right” analytics rate from 65% to 92% through improved data context and understanding provided by their enterprise data catalog
- JPMorgan Chase reduced data preparation time for their analytics team by 64% after implementing a self-service data catalog, allowing them to deliver insights twice as fast
One particularly striking example comes from Unilever. Before implementing a unified data catalog, their marketing analytics required data from seven different systems, each with its own access process. A typical campaign analysis took three weeks to assemble data before actual analysis could begin. After implementation, marketers could self-serve 90% of their data needs and begin analysis within hours.
The transformation isn’t just about speed—it’s about fundamentally changing how data serves the business.
In the next section, we’ll address common challenges organizations face when implementing self-service data catalogs and strategies to overcome them.
Challenges and Solutions
While the benefits of implementing a data catalog are compelling, the journey isn’t without obstacles. Here are the most common challenges enterprises face when transitioning to self-service analytics and strategies to overcome them.
Challenge 1: Data Quality and Trust Issues
Problem: Users may discover data through the catalog but find it incomplete, outdated, or inconsistent, undermining trust in the self-service model.
Solutions:
- Implement data quality monitoring and surface quality metrics directly in the catalog
- Create a certification process for high-value datasets that meet quality standards
- Enable user feedback and ratings to highlight reliable datasets
- Connect lineage information to help users understand data origins and transformations
Organizations like Netflix have successfully addressed this by implementing quality scores visible in their data catalog and establishing clear ownership for each dataset to ensure quality maintenance.
Challenge 2: Balancing Governance with Accessibility
Problem: Overly strict governance policies can negate self-service benefits, while too little governance creates compliance and security risks.
Solutions:
- Adopt a tiered governance approach with different levels of control based on data sensitivity
- Use attribute-based access control to dynamically determine access rights
- Implement monitoring and audit trails to detect potential misuse
- Create clear, transparent policies written in business language
Capital One has mastered this balance by implementing what they call “freedom within a framework”—clear guardrails that still enable broad self-service access for appropriate use cases.
Challenge 3: Cultural Resistance
Problem: Both data teams accustomed to controlling access and business users comfortable with the request process may resist the new self-service paradigm.
Solutions:
- Demonstrate early wins with metrics showing time saved for both data teams and business users
- Provide comprehensive training tailored to different user personas
- Establish a center of excellence to provide ongoing support
- Create incentives for data teams to enable rather than gate-keep
Microsoft overcame internal cultural resistance by measuring and showcasing how their data catalog reduced time-to-insight from weeks to hours, convincing even the most skeptical stakeholders.
Challenge 4: Metadata Management at Scale
Problem: As your data estate grows, manually maintaining comprehensive, accurate metadata becomes impossible.
Solutions:
- Leverage automated scanners and AI to extract and maintain technical metadata
- Implement workflows that capture metadata during data creation rather than after the fact
- Use machine learning to enrich metadata with tags and categorizations
- Build crowdsourcing capabilities for business context and tribal knowledge
Spotify successfully manages metadata at scale by combining automated scanners with collaborative features that enable data producers and consumers to continually improve descriptions and context.
Challenge 5: Integration with Existing Workflows
Problem: If accessing the catalog requires users to leave their familiar tools and environments, adoption will suffer.
Solutions:
- Implement catalog integrations with popular BI tools, notebooks, and data science platforms
- Create plugins for collaboration platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams
- Develop APIs that allow custom applications to leverage catalog functionality
- Ensure catalog features appear natively within existing data workflows
Uber drove rapid adoption by ensuring their data catalog was accessible directly from within their most popular analysis tools, making discovery a seamless part of existing workflows rather than a separate step.
By anticipating and addressing these challenges proactively, enterprises can significantly increase the likelihood of successful transformation to a self-service model powered by a modern data catalog.
Conclusion: The Future of Enterprise Data Access
The days of month-long wait times for basic data access are coming to an end. Modern data catalogs like Unity Catalog are ushering in a new era where business users can independently discover, understand, and access the data they need—while maintaining proper governance and security.
This transformation delivers benefits across the organization:
- Business users gain agility and autonomy, able to answer their own questions without lengthy delays
- Data teams can focus on complex analytics and innovation rather than servicing routine data requests
- Organizations become more data-driven, making decisions based on facts rather than gut feeling
- Security and compliance are enhanced through consistent, transparent policies across the data estate
The journey to self-service analytics is not just a technical implementation—it’s a fundamental shift in how organizations think about and work with data. Those who successfully make this transition gain (in time) a significant competitive advantage: the ability to move at the speed of business rather than the speed of their data request backlog and data infrastructure.
As we look to the future, emerging capabilities like AI-assisted data discovery, automated quality monitoring, and natural language interfaces will make self-service analytics even more accessible to non-technical users. Organizations that establish strong data catalog foundations today will be well-positioned to leverage these advancements.